File Pdf : Compressor-GM35AF-GM55AF-GM70AF-GM66AF-GM75AF-GM77AF-GM80AF-GM91AF-GM80AF


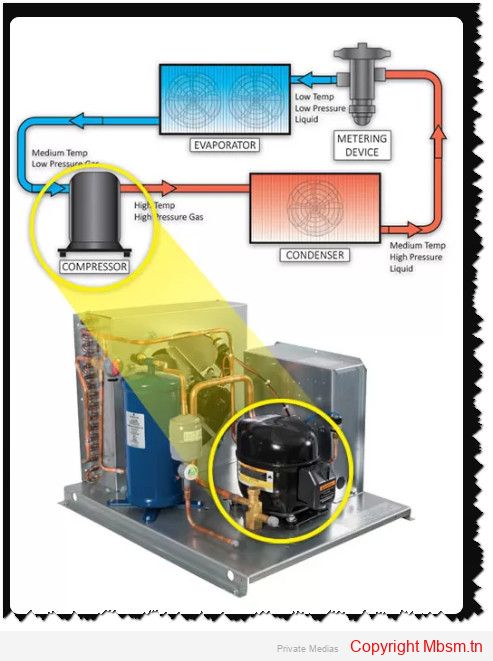
Temperature control plays a crucial role in the performance and efficiency of refrigeration systems, particularly in relation to compressor operation. The compressor is a vital component that significantly influences the overall energy consumption and effectiveness of the refrigeration cycle. Understanding how temperature affects compressor performance can lead to improved energy efficiency and system reliability.
1. Coefficient of Performance (CoP)
The Coefficient of Performance (CoP) is a primary measure of the efficiency of refrigeration systems, defined as the ratio of useful cooling provided to the work input by the compressor. A higher CoP indicates better energy efficiency. The CoP is influenced by two main temperatures: the evaporating temperature (TeTe) and the condensing temperature (TcTc). Specifically, an increase in TeTe or a decrease in TcTc enhances the CoP, with each 1°C change in these temperatures resulting in a 2-4% variation in energy use for constant cooling output
1.2. Operating Pressures
Operating pressures are closely linked to temperature control. Higher operating pressures improve heat transfer rates, which enhances overall system efficiency and reduces energy consumption. Conversely, low operating pressures can lead to increased energy usage as the compressor must work harder to achieve desired cooling effects3. This relationship underscores the importance of maintaining optimal pressure levels for effective temperature control.3. Variable Speed Compressors
The implementation of variable speed compressors allows for dynamic adjustment based on cooling demands. This adaptability helps maintain optimal performance across varying load conditions, thus improving CoP at partial loads12. For instance, reducing compressor speed can lead to significant energy savings while still meeting cooling requirements2.
1. Adjusting Evaporating and Condensing Temperatures
Practical measures to optimize TeTe and TcTc include:
2. Enhanced Control Systems
Advanced control strategies that monitor parameters such as two-phase length and superheat temperature can optimize compressor operation. These systems can dynamically adjust compressor speed to maintain desired cooling capacities while maximizing efficiency
2.3. Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance of refrigeration systems is essential to ensure that all components, including compressors, operate efficiently under varying temperatures. This includes cleaning heat exchangers and ensuring that expansion valves are properly set to minimize superheating1.
Temperature control is integral to optimizing compressor performance in refrigeration systems. By understanding the relationships between evaporating and condensing temperatures, operating pressures, and compressor dynamics, significant improvements in energy efficiency can be achieved. Implementing advanced controls and maintaining optimal operating conditions are essential strategies for enhancing the overall performance of refrigeration systems.

Refrigeration compressors are essential components in cooling systems, and understanding common issues can help in troubleshooting and maintaining their efficiency. Below are some prevalent problems, their causes, and potential solutions.
Regular maintenance and prompt troubleshooting of these common issues can significantly enhance the lifespan and efficiency of refrigeration compressors. Implementing a preventive maintenance schedule will help mitigate many of these problems before they escalate into major repairs.
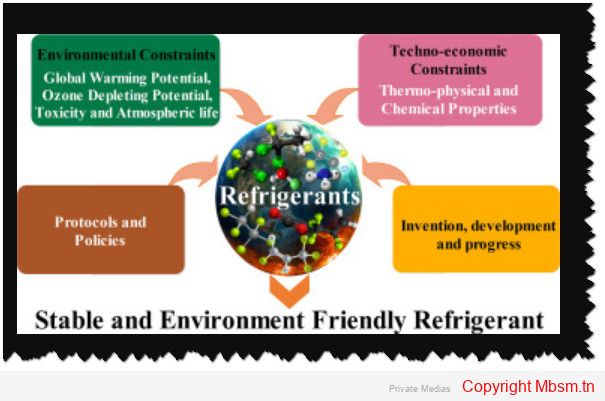
Refrigerants play a crucial role in the efficiency of cooling systems, particularly in vapor compression refrigeration cycles. This analysis focuses on two commonly used refrigerants: R134A (tetrafluoroethane) and R600A (isobutane). Both refrigerants have distinct properties that influence their performance in various applications, including air conditioning and refrigeration.Cooling Capacity and Coefficient of Performance (COP)
Thermophysical Properties
Environmental Impact
Applications and Trends
In conclusion, both R134A and R600A have unique advantages and limitations that affect their performance in cooling systems. While R134A offers higher efficiency and cooling capacity, R600A presents a more environmentally friendly option with specific safety considerations. The choice between these refrigerants will increasingly depend on balancing performance needs with environmental responsibilities.